Since 2022, many analysts have been forecasting a recession in the United States. However, once again this year, the world's leading economy has escaped the recessionary scenario anticipated by players in the US financial sector.
In this article, we'll try to understand how a recession manifests itself and how long it takes to materialize.
As a reminder, recessions are often beneficial for gold price growth.
What is a recession (definition)?
A recession is a temporary period of economic decline during which a country's economic activity slows significantly. It is generally characterized by several factors:
- Decline in GDP: The country's gross domestic product (GDP) is declining for at least two consecutive quarters.
- Rising unemployment: The unemployment is increasing as companies cut back on production and therefore on workforce.
- Reduced consumer spending: Consumers are spending less on goods and services, which has a negative impact on businesses.
- Falling investment: Businesses and individuals are investing less.
- Falling economic confidence: Consumer and business confidence in the economy is falling.
Chronology of a recession
1. Warning signs:
Warning signs of a recession can include an inversion of the yield curve (where short-term interest rates become higher than long-term rates), a drop in consumer and business confidence, and a reduction in investment expenditure.
To spot warning signs, it is also crucial to monitor Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) in both the services and manufacturing sectors. In general, the service sector is more resilient than the manufacturing sector. When a recession is confirmed, both sectors simultaneously fall below 50 in the PMI index (indicating an economic contraction).
2. Triggering:
Recession is often triggered by a series of economic shocks or restrictive monetary policies, as was potentially the case in 2022 after one of the fastest rate hikes in US history.
GDP begins to shrink, leading to higher unemployment and reduced consumer spending.
3. Duration:
The duration of a recession can vary considerably. Historically, previous recessions have lasted from a few months to several years. For example, the 2008 recession lasted around 18 months, while the 2020 Covid recession was particularly rapid, lasting just a few months.
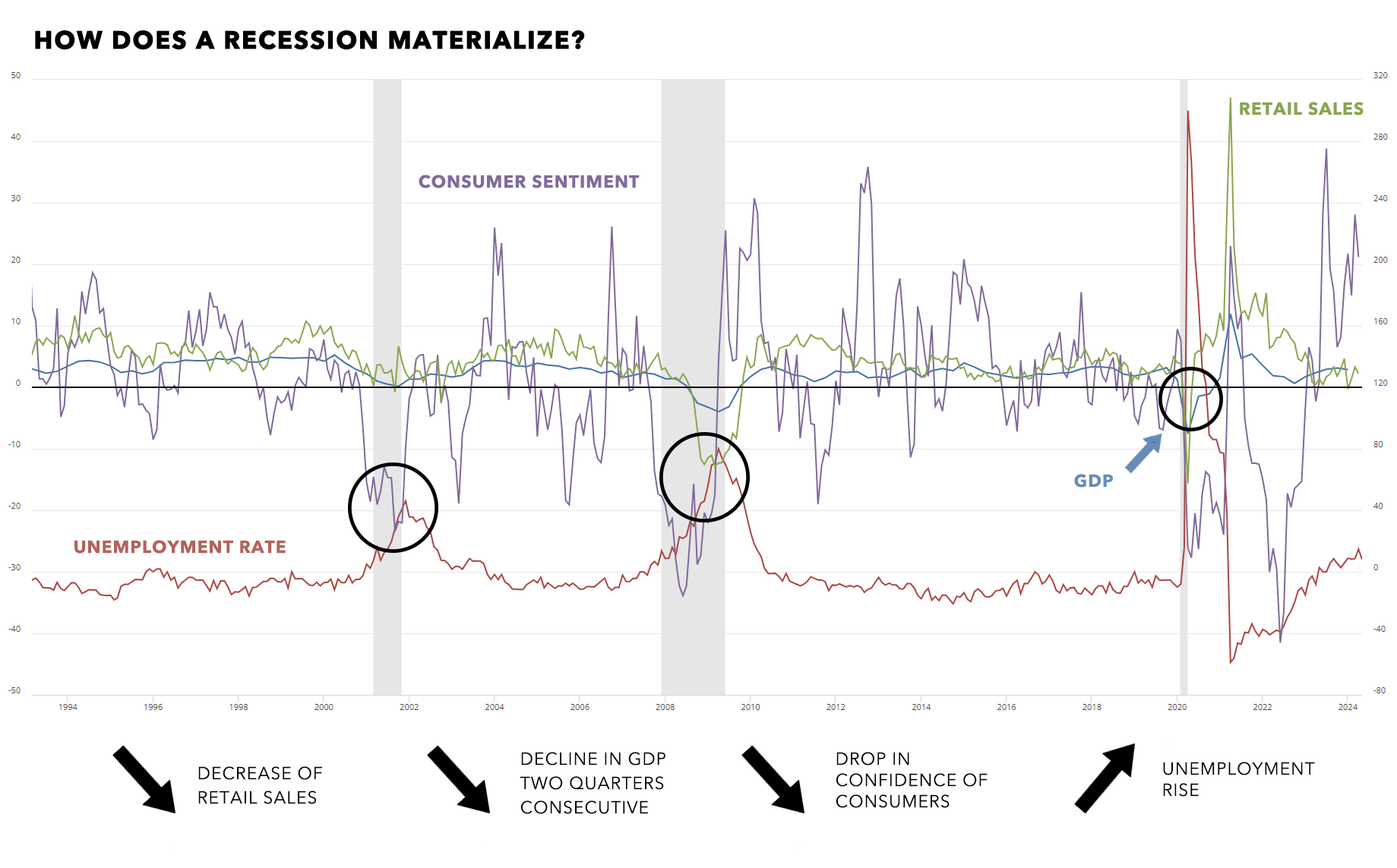
How does a recession materialize?
What's the current situation?
In the United States, we are currently seeing economic resilience despite predictions of a recession in 2022. Indeed, many portfolio managers and analysts had warned of a possible recession that year, but events have not unfolded as expected.
The situation is particularly mixed: key indicators such as the unemployment rate remain relatively low. After the Covid-19 period, the situation is normalizing.
The labor market is showing signs of weakness, with a slight rise in the unemployment rate to around 4%. However, what is most striking is the increase in part-time employment, while full-time jobs are declining. This trend is contributing to the current economic uncertainty.
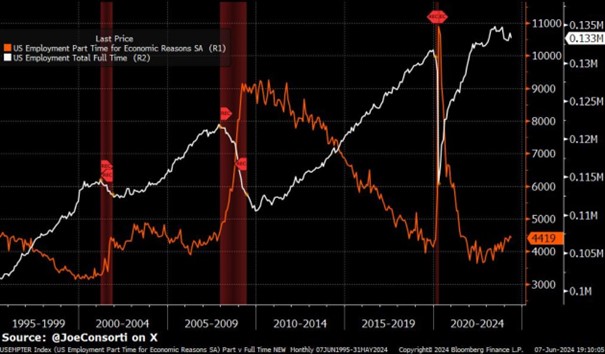
Part-time jobs (orange) / Full-time jobs (white) I Bloomberg
For the time being, household consumption is not showing any marked signs of weakness. However, this is strongly contrasted by the fact that many Americans are getting into debt through revolving credits with rates oscillating around 20%, in order to be able to maintain their consumer spending after the rise in inflation that occurred in April 2021.
Historical examples and their chronology
1. The Great Depression (1929-1933)
The Great Depression is the most emblematic example of a prolonged recession, beginning with the stock market crash of October 1929. Industrial production, world trade and GDP fell dramatically. Unemployment in the US reached around 25% in 1933. This recession lasted almost four years before aggressive political measures and the Second World War stimulated an economic recovery.
2. The subprime crisis
The global financial crisis, also known as the Great Recession, began in 2008 with the collapse of Lehman Brothers and the subprime crisis.
It led to a severe contraction in global economic activity. In the United States, GDP fell by 4.3% between the fourth quarter of 2007 and the second quarter of 2009. Unemployment peaked at 10% in October 2009.
This recession lasted around 18 months, with its effects being felt for several years afterwards.
To conclude
For now, economic growth in the United States appears to be slowing without entering recession. The Federal Reserve is keeping inflation under control, which could eventually lead to interest rate cuts from the end of 2024 if economic data continues on its current trajectory.
Yet Bloomberg's Economic Surprises Index, which measures whether economic data came in above or below Wall Street's average estimates, is at its lowest since 2019, underscoring the fragility of the economy as a whole. However, the prospects of rate cuts are boosting financial markets to record highs. Sometimes, bad economic data can be favorable to the markets, thus illustrating the complexity of the stock markets.
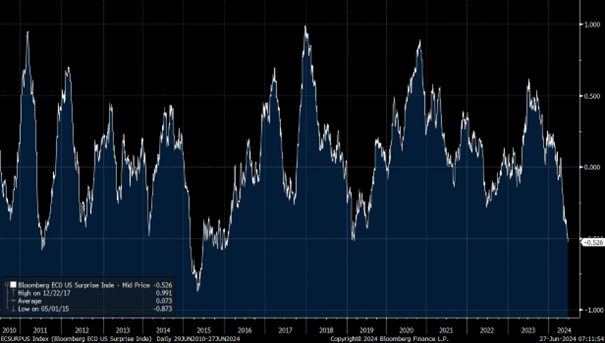
Economic Surprises Index I Bloomberg
In my opinion, in increasingly concentrated financial markets, which are approaching the bubble levels seen in the past, and with the dollar likely to lose its status as the world's store of value sooner or later (we are seeing with de-dollarization and the expansion of BRICS), it seems crucial to allocate a portion of your diversified portfolio to physical gold.
Stock markets are not currently attractive, as confirmed by the risk premium, which remains close to its 20-year lows.
Gold, the Asset of Choice in Recessionary Times? (@HimoraSlimane)
— GoldBroker (@Goldbroker_com) December 20, 2023
➡ https://t.co/8BQYmSggsj#recession #rates #inflation #gold #wealth #investing pic.twitter.com/8Vg6saS818
Reproduction, in whole or in part, is authorized as long as it includes all the text hyperlinks and a link back to the original source.
The information contained in this article is for information purposes only and does not constitute investment advice or a recommendation to buy or sell.